Have you caught yourself doing this? You skip Google, ignore Bing, and ask ChatGPT to get a straight answer to something on your mind? Just the info you need, neatly summarized.
And then it hits you: How can my business become a part of that experience? How do you make sure your content stays visible in traditional search results while also being cited in AI-powered search responses? That’s the question Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is here to answer because the rules of search have changed.
Let’s dive into our article, we’ll take you beyond just understanding what GEO is. You will discover how GEO differs from SEO, along with the winning GEO strategies you need to stay visible in an AI-driven world. All backed by insights, research, and real-world knowledge from our experienced SEO experts.
What are generative engines?
It’s common knowledge, Generative engines (GEs), often called AI-powered search engines, are designed to generate direct, contextual answers based on how people ask questions, whether by voice, image, or typed prompt.
There are two types of GE: AI-powered search engines that crawl the web independently, and AI chatbots that rely on external search data.
AI-powered search engines
AI-powered search engines like Google, Bing, Perplexity... are platforms that retrieve and generate results based on their own crawling and indexing systems. They use proprietary bots to scan the web, store relevant information, and respond to user queries without relying on third-party integrations. These engines combine traditional search infrastructure with large language models (LLMs) that can interpret user intent, enabling them to generate fast, personalized, and contextually relevant answers.
AI chatbots integrated with search
AI chatbots integrated with search like ChatGPT, Gemini,... are conversational tools that utilize LLMs to generate human-like responses. These chatbots rely on external search engines, such as Google or Bing, to fetch real-time information. They access and interpret data using APIs or plugin systems, enabling them to provide up-to-date responses without maintaining their own web index.
How AI-powered search engines differ from traditional search engines
To see why AI search is gaining ground, it helps to first understand where traditional search engines fall short.
What’s the gap with conventional search?
You might rethink of conventional search engines! As highlighted in Google's update on AI search evolution, these engines are struggling to keep up with the scale and behavior of today’s digital landscape.
- The sheer volume of data online makes it hard for traditional algorithms to crawl, process, and rank information efficiently without more advanced methods like machine learning or natural language processing (NLP).
- Search engines interpret queries literally, which means small errors - like typing “pziza” instead of “pizza” - often result in irrelevant or no results unless that exact typo exists in the index.
- Results pages are increasingly cluttered with ads and SEO-manipulated content, which pushes genuinely helpful answers further down or out of sight completely.
- Social media platforms have emerged as discovery engines, with fast, visual-first content now shaping how users, especially younger ones, find information and make decisions.
These gaps opened the door for AI-powered systems designed to understand real user intent, not just keywords.
How AI-powered search fills the gap?
AI-powered search engines fill the shortcomings of traditional search. They don’t just look for keywords - they decode the meaning behind a query and tailor the response to the individual.
- Enhanced understanding of user intent allows these systems to return meaningful results even when queries are vague, conversational, or unconventional.
- Personalization through behavioral analysis helps deliver content that aligns with a user’s preferences, past interactions, and search context, improving satisfaction and trust.
- A more intuitive experience is made possible through features like voice search, visual lookup, and instant answers, reducing friction and removing the need for multiple clicks.
- Continuous learning and adaptation ensures that the engine improves with every interaction, becoming smarter, faster, and more precise over time.
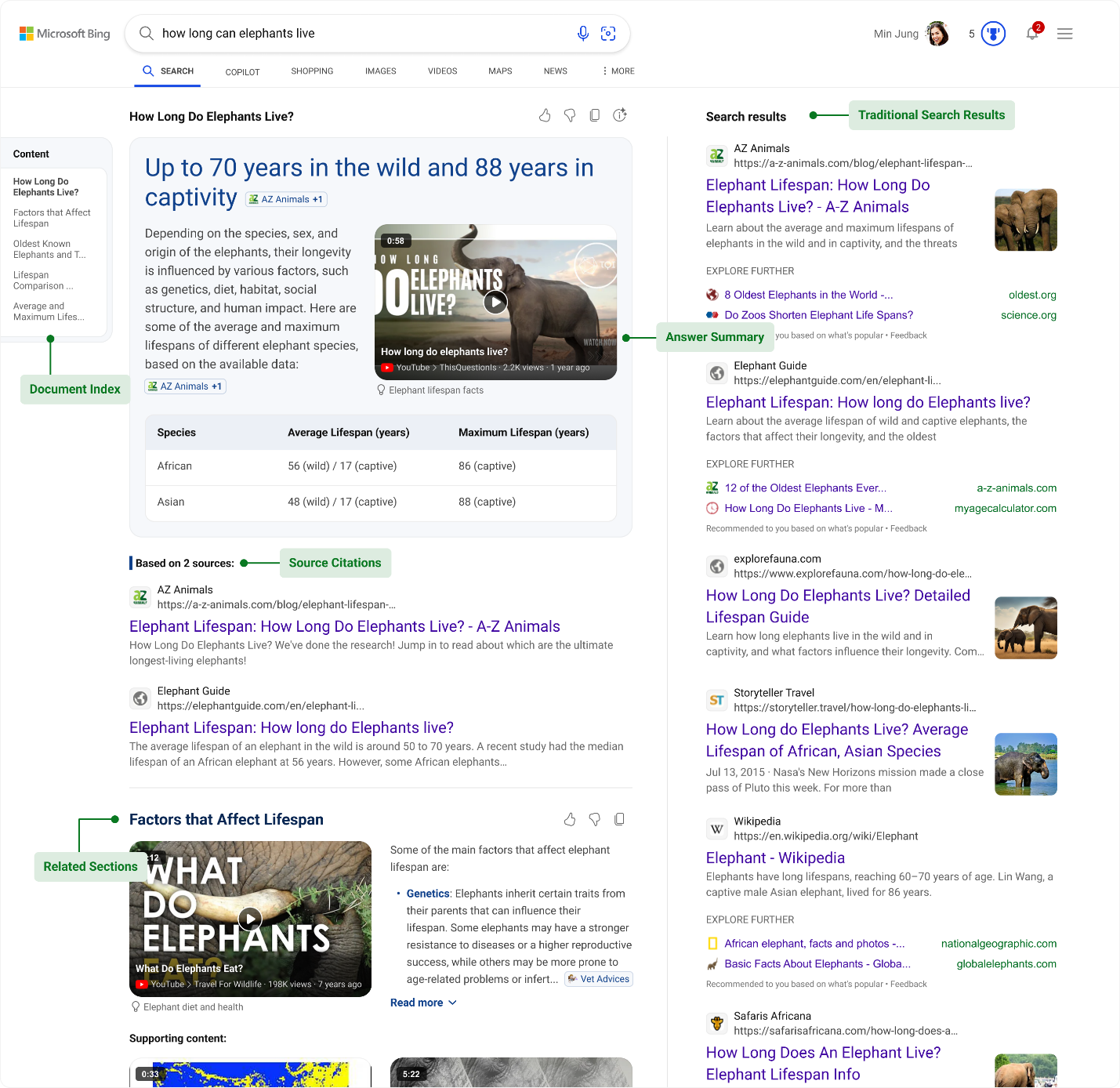
The difference between traditional search result and AI generated result on Bing. Source: Bing Blogs
SEO vs GEO
GEO and SEO both aim to increase online visibility, but they target fundamentally different search environments and use slightly distinct strategies:
|
Aspect |
SEO (Traditional) |
GEO (Generative engine optimization) |
|
Goal |
Rank higher in search results for clicks and traffic |
Be cited or included in AI-generated responses |
|
Success metrics |
Rankings, organic traffic, click-through rates |
Citation frequency, inclusion in AI responses, clicks from citation |
|
Optimization focus |
Keywords, backlinks, technical SEO, user experience |
Same as SEO, plus: Content structure, factual accuracy, clarity, multiple perspective covering |
|
Technical emphasis |
Crawlability, indexability, site speed, mobile friendly |
Same as SEO, plus: JavaScript Rendering caution |
SEO and GEO are deeply interconnected. Traditional SEO forms the baseline that GEO builds upon. Without proper crawlability, indexability, and technical structure, AI systems can’t even access or evaluate your content.
Crawling and indexing still matter. Generative engines need to find and understand content the same way traditional search engines do. If your content isn’t structured well or is buried behind scripts AI can’t parse, it’s unlikely to be cited. This reinforces the value of technical SEO for crawlability and indexability.
Where things diverge is in how content is ranked or cited. Traditional search ranks results based on relevance and authority signals in a list format. Generative engines select content to synthesize and present as a unified answer.
That means the best-ranked SEO page might not appear in a Google AI Overview.
For example, a top 3 Google search result may not appear in an AIO (AI Overview) answer. Similarly, ChatGPT might cite a source that appears in Bing Copilot’s response - even if both are drawing from the same dataset. That’s because each platform uses its own model to decide what content to reference, how to format the response, and what source gets attribution. To succeed, brands must adopt tailored strategies.
GEO isn’t a replacement for SEO - it’s an evolution. Getting cited in AI-generated results starts with the same foundation, but requires new thinking about how, where, and why your content appears.
GEO strategies
Getting cited in AI responses requires a strategic pivot. Here are the must-do GEO strategies that can make or break your visibility.
Tailoring GEO to each platform
GEO strategies must be tailored for each AI platform, as no two platforms operate the same way. Each uses different algorithms, ranking logic, and citation methods, which means a one-size-fits-all approach won’t work. Your strategy should begin by identifying which platforms your audience uses most frequently because GEO success depends heavily on targeting the right audience on the right platform.
However, the number and type of users across other platforms differ and that should influence your platform focus. Here’s a quick comparison:
|
AI Platform |
Audience |
Reach |
||
|
|
Full-time workers, homemakers, retirees
|
|
||
|
ChatGPT |
Gen Z, students, younger male users
|
4.46 billion monthly visits
|
||
|
Bing |
College graduates, most popular with ages 25–34
|
Over 5.28 billion monthly visits (Meetanshi) |
If your target users include younger people, it’s strategic to prioritize platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, or even social discovery engines like Reddit, TikTok, and Quora. If you’re targeting working professionals or older demographics, optimizing for Google and Bing may yield better visibility. Your GEO strategy should always reflect where your audience actually searches.
If resources are limited, it makes strategic sense to focus your GEO efforts on Google’s ecosystem. Google alone accounts for 85.2 billion monthly visits (Search Enduance), far outpacing other platforms. Google remains the primary gateway for most users across all age groups and continues to integrate AI deeply across its services. By focusing your GEO strategy on Google, you're more likely to gain visibility not just in Search, but also in its expanding ecosystem.
SEO is foundation of GEO
Traditional SEO practices like crawlability, indexability, and site performance are still essential. Without them, your content might never be found or processed by either traditional search engines or AI-driven platforms.
But GEO builds on top of those fundamentals. Generative engines don’t just rank pages, they generate responses. For your content to be included in AI outputs, it must be well-structured, factually accurate, and clear enough for a machine to interpret and trust. This means investing in schema markup, semantic HTML, and strong internal linking.
Think of SEO as the groundwork and GEO as the next layer. One ensures you’re visible. The other ensures you’re cited.
Universal strategies for all AI-powered search engines
While each AI platform has its own quirks, there are foundational GEO strategies that work across the board:
- Focus on user intent and context, not just exact-match keywords. Write content that directly answers questions in a natural, conversational tone.
- Structure your content clearly with headers, lists, tables, and visuals to help both AI and human readers understand and navigate it.
- Use schema markup where relevant (FAQs, products, articles, organization, itemList) to help AI engines interpret your content more accurately.
- Encourage user engagement through quality content that keeps people on the page, sparks sharing, and builds trust - signals that AI may use to evaluate usefulness.
- Build authority using E-E-A-T: Show real-world experience, cite expert sources, use trusted authors, and earn backlinks.
- Monitor AI answers regularly to see how your content appears in tools like ChatGPT, Copilot, or Perplexity, and adjust based on what’s consistently being cited. Stay adaptable as AI and LLM algorithms update, which may change how content is surfaced, interpreted, or attributed.
AI-powered search engine optimization checklist
To bring your AI SEO and GEO strategy to life, here’s a practical checklist of core tasks and recommended tools that apply across most AI-powered search engines:
|
Task |
Tools |
|
Semantic keyword research |
Follow-up question, People also ask, People also search |
|
Schema markup implementation* |
Google Rich Result, schema.org |
|
Page speed optimization |
PageSpeed Insights |
|
Authority building |
Ahrefs, SEMrush |
|
AI monitoring and adaption |
All AI Search platforms, Google Search Console, Google Analytics, Bingwebmaster |
Explore how our AI‑powered offerings are structured to support Generative Engine Optimization strategies.
Conclusion
AI-powered search has fundamentally changed how people find and consume information. GEO is not just a nice-to-have, it is essential for staying visible in a landscape where answers are generated, not just linked. Brands that fail to adapt risk disappearing from the conversation altogether.
SEO sets the stage, but GEO takes it further with strategies tailored for AI engines. It demands content that is structured, factual, and optimized for how AI engines interpret and synthesize data.
If your business wants to stay ahead of the curve, now is the time to act. Learn how Niteco’s AI SEO services can help you build a GEO strategy that ensures your brand shows up in the future of search.
FAQ
Generative engine optimization complements traditional SEO by extending your brand’s reach into the emerging world of AI-driven search. The benefits include greater visibility, improved engagement with the questions people ask, frequent brand mentions and high-quality traffic from users guided by AI.
- Use Google Analytics or another analytics tool to segment referral traffic from AI sources (e.g, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini...). Analyze CTR, conversions, and user behavior from AI-driven visitors.
- Compare the AI-driven results to the standard search snippet to see if AI-generated answers drive more or fewer results in Google Search Console
- Monitor your domain authority and new external links pointing to your website via SEO 3rd party tool such as Semrush, Ahref
- Manually track AI-generated responses by searching for your keyword targets
With upgraded features and additional setup, conventional SEO tools still support GEO. For example, tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console can be used for tracking and analysis. ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other generative engines (GE) can assist with content creation and task management. SEO platforms such as Ahrefs and SEMrush can help track and enhance AI visibility, conduct keyword research, perform market research, and analyze competitors.



